Video display controller
This articleneeds additional citations forverification.(December 2015) |

Avideo display controller(VDC), also called adisplay engineordisplay interface,is anintegrated circuitwhich is the main component in avideo-signal generator,a device responsible for the production of aTVvideo signalin a computing or game system. Some VDCs also generate anaudio signal,but that is not their main function. VDCs were used in thehome computersof the 1980s and also in some earlyvideo picturesystems.
The VDC is the main component of the video signal generator logic, responsible for generating the timing of video signals such as the horizontal and verticalsynchronization signalsand theblanking intervalsignal. Sometimes other supporting chips were necessary to build a complete system, such asRAMto holdpixeldata,ROMto holdcharacter fonts,or somediscrete logicsuch asshift registers.
Most often the VDC chip is completely integrated in the logic of the main computer system, (itsvideo RAMappears in thememory mapof the main CPU), but sometimes it functions as acoprocessorthat can manipulate the video RAM contents independently.
Video display controller vs. graphics processing unit[edit]
The difference between a display controller, a graphics accelerator, and a video compression/decompression IC is huge, but, since all of this logic is usually found on the chip of agraphics processing unitand is usually not available separately to the end-customer, there is often much confusion about these very different functional blocks.
GPUs with hardware acceleration became popular during the 1990s, including theS3 ViRGE,theMatrox Mystique,and theVoodoo Graphics;though earlier examples such as theNEC μPD7220had already existed for some time. VDCs often had special hardware for the creation of "sprites",a function that in more modern VDP chips is done with the"Bit Blitter"using the"Bit blit"function.
One example of a typical video display processor is the "VDP2 32-bit background and scroll plane video display processor"of theSega Saturn. Another example is theLisa(AGA) chip that was used for the improved graphics of the later generationAmigacomputers.
That said, it is not completely clear when a "video chip" is a "video display controller" and when it is a "video display processor". For example, the TMS9918 is sometimes called a "video display controller" and sometimes a "video display processor". In general however a "video display processor" has some power to "process" the contents of the video RAM (filling an area of RAM for example), while a "video display controller" only controls the timing of the video synchronization signals and the access to the video RAM.
Thegraphics processing unit(GPU) goes one step further than the VDP and normally also supports 3D functionality. This is the kind of chip that is used in modern personal computers.
Types[edit]
Video display controllers can be divided in several different types, listed here from simplest to most complex;
- Video shifters,or "video shift register based systems" (there is no generally agreed upon name for these type of devices), are the most simple type of video controllers. They are directly or indirectly responsible for the video timing signals, but they normally do not access the video RAM directly. They get the video data from the main CPU, a byte at a time, and convert it to a serial bitstream, hence the technical name "video shifter". This serial data stream is then used together with the synchronization signals to output a video signal. The main CPU needs to do the bulk of the work. Normally these chips only support a very low resolutionraster graphicsmode.
- ACRTC,orcathode-ray tubecontroller, generates the video timings and reads video data from RAM attached to the CRTC to output it via an external character generator ROM (fortext modes) or directly to the video output shift register (for high resolution graphics modes).[1]Because the actual capabilities of the video generator depend to a large degree on the external logic, video generator based on a CRTC chip can have a wide range of capabilities, from simple text-mode only systems to high-resolution systems supporting a wide range of colours. Sprites, however, are normally not supported by these systems.
- Video interface controllersare much more complex than CRT controllers, and the external circuitry that is needed with a CRTC is embedded in the video controller chip. Sprites are often supported, as are (RAM based)character generatorsand video RAM dedicated tocolour attributesandpallette registers(colour lookup tables) for the high-resolution or text modes.
- Video coprocessorshave their own internal CPU dedicated to reading (and writing) their own video RAM (which may be shared with the CPU), and converting the contents of this video RAM to a video signal. The main CPU can give commands to the coprocessor, for example to change the video modes or to manipulate the video RAM contents. The video coprocessor also controls the (most often RAM-based) character generator, the colour attribute RAM, palette registers, and the sprite logic (as long as these exist of course).
List of example VDCs[edit]
Examples of video display controllers are:
Video shifters
- TheRCA CDP1861was a very simple chip, built inCMOStechnology (which was unusual for the mid-1970s) to complement theRCA 1802microprocessor, it was mainly used in theCOSMAC VIP.It could only support a very low resolution monochrome graphic mode.
- TheTelevision Interface Adaptor(TIA) is the custom video chip that is the heart of theAtari 2600games console, a primitive chip that relied on the 6502 microprocessor to do most of the work, also was used to generate the audio.
CRT Controllers
- TheIntel 8275CRT controller was used in theConvergent TechnologiesAWS /Burroughs B20,along with someS-100 bussystems.
- TheMotorola 6845(MC6845) is a video address generator first introduced byMotorolaand used for theAmstrad CPC,and theBBC Micro.It was also used for almost all the early video adapters for the PC, such as theMDA,CGAandEGAadapters. The MDA and CGA use an actual Motorola chip, while the EGA has a custom IBM chipset of five LSI chips; one of those chips includes IBM's reimplementation of the CRTC, which operates like an MC6845 but differs in a few register addresses and functions so it is not 100% compatible. In all laterVGAcompatible adapters the function of the 6845 is still reproduced inside the video chip, so in a sense all currentIBM PC compatiblePCs still incorporate the logic of the 6845 CRTC.
Video interface controllers
- TheSignetics 2636and2637are video controllers best known for their use in theInterton VC 4000andEmerson Arcadia 2001respectively.
- TheMC6847is a video display generator (VDG) first introduced by Motorola and used in theTRS-80 Color Computer,Dragon 32/64,Laser 200andAcorn Atomamong others.
- TheMOS Technology 6560 (NTSC) and 6561 (PAL)are known as the video interface controller (VIC) and used in theVIC-20.
- TheMOS Technology 6567/8562/8564 (NTSC versions) and 6569/8565/8566 (PAL)were known as the VIC-II and were used in theCommodore 64.
- TheMOS Technology 8563/8568was used in theCommodore 128(8563) and Commodore 128D (8568) to create an 80 column text display, as well as several high resolution graphics modes. The Commodore 128 models included aVIC-IIto supportCommodore 64compatible video modes.
- TheMOS Technology 7360text editing device (TED) was used in theCommodore Plus/4,Commodore 16andCommodore 116computers and had an integrated audio capability.
- ThePhilips semiconductorsSCC66470 was a VSC (Video- and Systems Controller) used in conjunction with their68070-Microcontroller e.g. inCD-isystems.
Video coprocessors
- TheANTIC(Alpha-NumericTelevisionInterfaceCircuit) was an early video system chip used inAtari 8-bit computers.It could read a "Display list"with its own built in CPU and use this data to generate a complex video signal.
- TheTMS9918is known as the Video Display Processor (VDP) and was first designed for theTexas InstrumentsTI-99/4,but was later also used in systems like theMSX(MSX-1),ColecoVision,Memotech MTX series,and for theSegaSG-1000andSC-3000.TheMaster Systemuses an enhanced VDP based on the TMS9918, and the Sega 315-5313 (Yamaha YM7101) VDP used in theSega Genesisand some arcade machines is a further advancement of the Master System VDP with the original (inferior) TMS9918 modes removed.
- TheNEC μPD7220.Used in some high-end graphics boards for the IBM PC in the mid 80s, notably in products fromNumber Nine Visual Technology.
- ThePicture Processing Unitwas a video coprocessor designed byRicohforNintendo's use in the Famicom andNintendo Entertainment System.It was connected to 2048bytesof dedicated video RAM, and had a dedicated address bus that allowed additional RAM or ROM to be accessed from the game cartridge. A scrollable playfield of 256×240 pixels was supported, along with a display list of 64 OBJs (sprites), of which 8 could be displayed per scanline.
- TheYamaha V9938is an improved version of the TMS9918, and was mainly used in theMSX2.
- TheYamaha V9958is the Video Display Processor (VDP) mainly used in theMSX2+andMSX turboRcomputers.
- The VLSI VS21S010D-L is a 128kB SPI/parallel SRAM with an integrated video display controller with variable-bit-depth pixels and a block-move blitter.
- TheThomson EF936xseries of Graphic Display Processor (GDP), which offers a draw rate of 1 millionpixelsper second and resolutions up to 1024×512.
Alternatives to a VDC chip[edit]
Note that many early home computers did not use a VDP chip, but built the whole video display controller from a lot ofdiscrete logicchips, (examples are theApple II,PET,andTRS-80). Because these methods are very flexible, video display generators could be very capable (or extremely primitive, depending on the quality of the design), but also needed a lot of components.
Many early systems used some form of an earlyprogrammable logic arrayto create a video system; examples include theZX SpectrumandZX81systems and ElektronikaBK-0010,but there were many others. Early implementations were often very primitive, but later implementations sometimes resulted in fairly advanced video systems, like the one in theSAM Coupé.On the lower end, as in the ZX81, the hardware would only perform electrical functions and the timing and level of the video stream was provided by the microprocessor. As the video data rate was high relative to the processor speed, the computer could only perform actual non-display computations during the retrace period between display frames. This limited performance to at most 25% of overall available CPU cycles.
These systems could thus build a very capable system with relatively few components, but the low transistor count of early programmable logic meant that the capabilities of early PLA-based systems were often less impressive than those using the video interface controllers or video coprocessors that were available at the same time. Later PLA solutions, such as those usingCPLDsorFPGAs,could result in much more advanced video systems, surpassing those built using off-the-shelf components.
An often-used hybrid solution was to use a video interface controller (often theMotorola 6845) as a basis and expand its capabilities with programmable logic or anASIC.An example of such a hybrid solution is the originalVGAcard, that used a 6845 in combination with an ASIC. That is why all current VGA based video systems still use thehardware registersthat were provided by the 6845.
Modern solutions[edit]
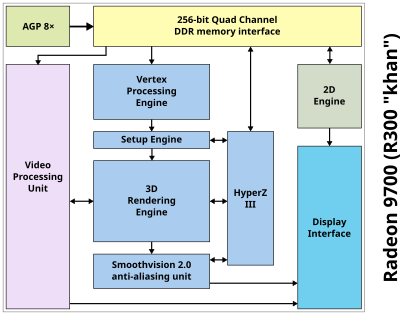
With the advancements made insemiconductor device fabrication,more and more functionality is implemented asintegrated circuits,often licensable assemiconductor intellectual property core(SIP core). Display controllerSystem In Package(SiP) blocks can be found on thedieofGPUs,APUsandSoCs.[citation needed]
They support a variety ofinterfaces:VGA,DVI,HDMI,DisplayPort,VHDCI,DMS-59and more. ThePHYincludesLVDS,TMDSandFlat Panel Display Link,OpenLDIandCML.[citation needed]
For example, a VGA-signal, which is created by GPU is being transported over a VGA-cable to the display controller. Both ends of the cable end in aVGA connector.Laptopsand othermobile computersuse different interfaces between the display controller and the display. A display controller usually supports multiplecomputer display standards.
KMS driveris an example of adevice driverfor display controllers andAMD Eyefinityis a special brand of display controller withmulti-monitorsupport.
RandR(resize and rotate) is a method to configure screen resolution and refresh rate on each individual outputs separately and at the same time configure the settings of the windowing system accordingly.
An example for this dichotomy is offered byARM Holdings:they offer SIP core for 3D rendering acceleration and for display controller independently. The former has marketing names such as Mali-200 or Mali-T880 while the latter is available as Mali-DP500, Mali-DP550 and Mali-DP650.[2]
History[edit]
In 1982,NECreleased theNEC μPD7220,one of the most widely used video display controllers in 1980spersonal computers.It was used in theNEC PC-9801,APC III,IBM PC compatibles,DEC Rainbow,Tulip System-1,andEpson QX-10.[3]Intellicensed the design and called it the 82720 graphics display controller.[4]
Previously, graphic cards were also called graphic adapters, and the chips used on theseISA/EISAcards consisted solely of a display controller, as this was the only functionality required to connect a computer to a display. Later cards included ICs to perform calculations related to 2D rendering in parallel with the CPU; these cards were referred to as graphics accelerator cards. Similarly, ICs for 3D rendering eventually followed. Such cards were available withVLB,PCI,andAGPinterfaces; modern cards typically use thePCI Expressbus, as they require much greater bandwidth then the ISA bus can deliver.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^M. Rasch, B. Bertelsons (1995). Scott Slaughter (ed.).PC Underground: Unconventional Programming Topics.US: Abacus Software Inc. p. 58-68.ISBN978-1557552754."Cathode Ray Tube Controller (CRTC) is responsible for generating the video signal and is programmable. CRTC-Registers bit meaning tables forVGA,EGA,CGA,Hercules,SVGA,Mode X."
- ^"Initial support for ARM Mali Display Controller".Linux kernel mailing list.2016-04-01.
- ^Dampf, Guido (1986)."Graphics with the NEC 7220: Direct access with Turbo Pascal".Retrieved27 July2013.(Translation of "Grafik mit dem 7220 von NEC",mc,1986, H11, pp. 54-65)
- ^Changon Tsay (January 1, 1986).A graphics system design based on the INTEL 82720 graphics display controller.University of Texas at El Paso. pp. 1–152.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)
External links[edit]
- Embedded Linux Conference 2013 – Anatomy of an Embedded KMS driveronYouTubeKMS driver is a device driver for display controllers
