Wyrrabalong National Park
| Wyrrabalong National Park New South Wales | |
|---|---|
 Northern section of the national park | |
| Nearest town or city | Gosford |
| Coordinates | 33°17′34.8″S151°32′34.8″E/ 33.293000°S 151.543000°E |
| Established | May 1991[1] |
| Area | 6.2 km2(2.4 sq mi)[1] |
| Managing authorities | NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service |
| Website | Wyrrabalong National Park |
| See also | Protected areas of New South Wales |

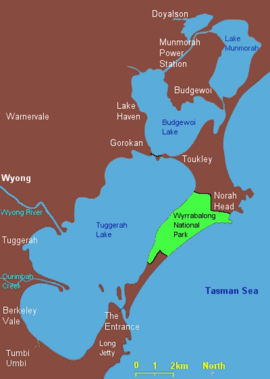
TheWyrrabalong National Parkis a coastalnational parkthat is located on theCentral CoastofNew South Wales,in easternAustralia.The 620-hectare (1,500-acre) national park consists of two sections; the northern section consists of approximately 480 hectares (1,200 acres) and covers a substantial area of the peninsula betweenThe EntranceandNorah Headas well as Terilbah and Pelican Islands withinTuggerah Lake.The southern section consists of about 120 hectares (300 acres) of the coast, fromShelly Beachsouth toForresters Beach.[2]The park is also noted for containing the last significant coastal (littoral) rainforest on the Central Coast.[3]
Most of the park lies in theTuggerahImportant Bird Area,identified as such byBirdLife Internationalbecause of its importance for a variety ofwaterandwoodlandbirds.[4]
The average elevation of the terrain is 8 metres.[5]
History
[edit]The land now occupied by Wyrrabalong National Park was first inhabited by theindigenousDarkinjungandAwabakalpeoples. The Darkinjung occupied the southern section and The Awabakal occupied the northern section. It is believedEuropeansfirstdiscoveredthe Tuggerah Lakesin 1796. It was found byGovernor of Tasmania,Colonel David Collins,who had arrived on theFirst Fleet,during the search for an escapedconvict,Mary Morgan, who was said to be living with the Aborigines to the North of theHawkesbury River.[6]
Weather
[edit]The average summer temperature is between 20 °C and 25 °C, and the record measured temperature is 42.4 °C, in winter the temperature is between 10 °C and 17 °C, and the lowest measured temperature is 3.4 °C.[7]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ab"Wyrrabalong National Park: Park management".Office of Environment and Heritage.Government of New South Wales.Retrieved4 October2014.
- ^Wyrrabalong National Park: Plan of Management(PDF).Government of New South Wales.25 March 2013.ISBN978-1-74359-198-7.Retrieved7 February2007.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^"Wyrrabalong National Park".Geographical Names Register (GNR) of NSW.Geographical Names Board of New South Wales.Retrieved11 August2013.
- ^"Tuggerah".Important Bird Areas factsheet.BirdLife International.2011. Archived fromthe originalon 30 June 2007.Retrieved17 November2011.
- ^"Wyrrabalong National Park topographic map, elevation, relief".topographic-map.Retrieved17 January2022.
- ^"Who Found Tuggerah Lake?".theentrancetcm.au.Retrieved18 July2006.
- ^"Wyrrabalong National Park | Visitor info".NSW National Parks.Retrieved16 January2022.
External links
[edit]- "Wyrrabalong National Park: Visitor guide".NSW National Parks and Wildlife Service(PDF brochure).Government of New South Wales.2012.

