Zoilus II
| Zoilus II Soter ( "The Saviour" ) | |
|---|---|
 Portrait of Zoilus II | |
| Indo-Greekking | |
| Reign | 55–35 BC |

Obv:Bust of Zoilus with Greek legend ΒΑΣΙΛΕΩΣ ΣΩΤΗΡΟΣ ΖΩΙΛΟΥ "Of King Zoilos the Saviour".
Rev:Athenaadvancing left, with thunderbolt and shield covered withaegis(type ofMenander I).Kharosthilegend: MAHARAJASA TRATARASA JHOILASA "King Zoilus the Saviour".
Zoilus II Soter(Ancient Greek:Ζωΐλος Σωτήρ,romanized:Zōïlos Sōtēr;epithetmeans "the Saviour" ) was anIndo-Greekking who ruled in easternPunjab.Bopearachchi dates his reign to c. 55–35 BC, a date approximately supported by R. C. Senior. It is possible that some of his coins were issued by a separate king, Zoilus III.
Rule[edit]


Zoilus seems to have been one of the rulers who succeeded the last important Indo-Greek kingApollodotus IIin the eastern parts of his former kingdom. All these kings use the same symbol as Apollodotus II, the fightingPallas Atheneintroduced by Menander I, and usually also the same epithetSoter(Saviour). It is therefore possible that they belonged to the same dynasty, and Zoilus II could also have been related to the earlier kingZoilus I,but the lack of written sources make all such conjections uncertain.
He may have been the Bactrian ally ofMark AntonyandCleopatra VIIreferred to byVirgilin his vision of theBattle of Actiumin:
Hinc ope barbarica variisque Antonius armis, |
Antony, with barbarous wealth and strange weapons, conqueror of eastern peoples and the Indian shores, bringing Egypt, |
| —Virgil,TheAeneid,8.688[1] |
Coinage[edit]
Zoilus II issued silver drachms with diademed portrait and Pallas Athene in rather crude style, and two sorts of bronzes in various denominations: "Apollo, with tripod and small elephant", and "Elephant and tripod".
Zoilus III, a separate king?[edit]

Obv:Bust of king with Greek legend ΒΑΣΙΛΕΩΣ ΣΩΤΗΡΟΣ ΖΩΙΛΟΥ "Of King Zoilos the Saviour".
Rev:Athenaadvancing left, with thunderbolt and shield covered withaegis(type ofMenander I).Kharosthilegend: MAHARAJASA TRATARASA JHOILASA "King Zoilus the Saviour".


The portraits attributed to Zoilus II could be divided into two groups; one depicting a balding man with hollow cheeks, the other a seemingly younger man with a fringe and round cheeks. As numismatic evidence indicates that the younger portraits are later, recent research has suggested that they be attributed to a younger king, Zoilus III Soter, who would then have been a son and successor of the older Zoilos.[2]
In particular, the mint mark which is characteristic of the coins of Zoilos with a full head of hair, is a later mint mark used down to the last Indo-Greek kingsStrato IIandStrato III,suggesting a later reign for Zoilus III.[2]This mint-mark however was never used by the "balding" Zoilus II, or by any king before him.[2]
Indo-Scythian imitations[edit]
TheIndo-ScythiankingBhadayasaalso copied coins of Zoilus II, or the hypothetical Zoilus III, only mentioning his own name on theKharoshthilegend of his coins.[2]
-
The "boxy" mint mark characteristic of Zoilus III and later Indo-Greek kings.
-
Another coin of the proposed Zoilus III.
-
Coin ofBhadayasa,an imitation of the proposed Zoilus IIII.
Monograms[edit]
Many of themonogramson the coins of Zoilus II are in Kharoshti, indicating that they were probably made by an Indian moneyer. This is a characteristic of several of the Indo-Greek kings of the eastern Punjab, such asStrato I,Apollodotus II,and sometimesApollophanesandDionysios.Furthermore, the monogram is often identical on their coins, indicating that the moneyer, or the place of mint, were the same.
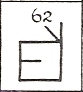
The coins of Zoilus II combine Greek monograms withKharoshthiones, indicating that some of thecelatorsmay have been native Indians. TheKharoshthimonograms are the letters for: sti, ji, ra, ga, gri, ha, stri, ri, bu, a, di, stra, and śi. The "Apollo and tripod" and "Elephant and tripod" types only have Kharoshthi monograms, while the portrait types usually have combinations of Greek and Kharoshthi monograms. The monogram 62 (below) has been shown to be the last Indo-Greek monogram, and only appears on the younger portraits that may belong to Zoilus III.
Findspots[edit]


The coins of Zoilus II have been found in theSutlejandSialkotII hoards, and inPunjabhoards east in theJhelum(Bopearachchi,p138).
Also, 25 coins of Zoilus II were found under the foundations of a 1st-century BC rectangular chapel in the monastery ofDharmarajika,nearTaxila.[3][4]
Two coins of Zoilus II were also found in the Bara hoard nearPeshawar,together with coins of the Indo-Scythian kingsAzes I,Azilises,Azes II.[5]
Overstrikes[edit]
A coin of Zoilus II was overstruck on a coin ofApollodotus II.
See also[edit]
- Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
- Seleucid Empire
- Greco-Buddhism
- Indo-Scythians
- Indo-Parthian Kingdom
- Kushan Empire
Notes[edit]
- ^Francis Henry SkrineandEdward Denison Ross,The Heart of Asia: A History of Russian Turkestan and the Central Asian Khanates from the Earliest Times,by London, Methuen, 1899, p.19; E. Drouin, “Bactriane”,La Grande Encyclopédie: Inventaire Raisonné des Sciences, des Lettres et des Arts,Paris, Lamirault, 1885-1902, Tome 4, pp.1115-1122, nb 1118.
- ^abcdJakobsson, J (2010). "A Possible New Indo-Greek King Zoilos III, and an Analysis of Realism on Indo-Greek Royal Portraits".Numismatic Chronicle.JSTOR article
- ^"Another group of coins which was found in greater numbers at religious sites, at Dharmarajika in particular, than at Sirkap is that of Zoilos II. A hoard of 25 drachms from the monastery are the only silver coins of Zoilos Soter found at Taxila" Numismatic Digest - Volume 4 - Page 13, 1980
- ^John Marshall, "Taxila, Archaeological excavations", p. 248 "The only minor antiquities of interest found in this building were twenty-five debased silver coins of the Greek king Zoilus II, which were brought to light beneath the foundations of the earliest chapel".)
- ^Reference
References[edit]
- The Greeks in Bactria and India,W. W. Tarn, Cambridge University Press.
- Indo-Greek Coins,R. B. Whitehead, 1914.