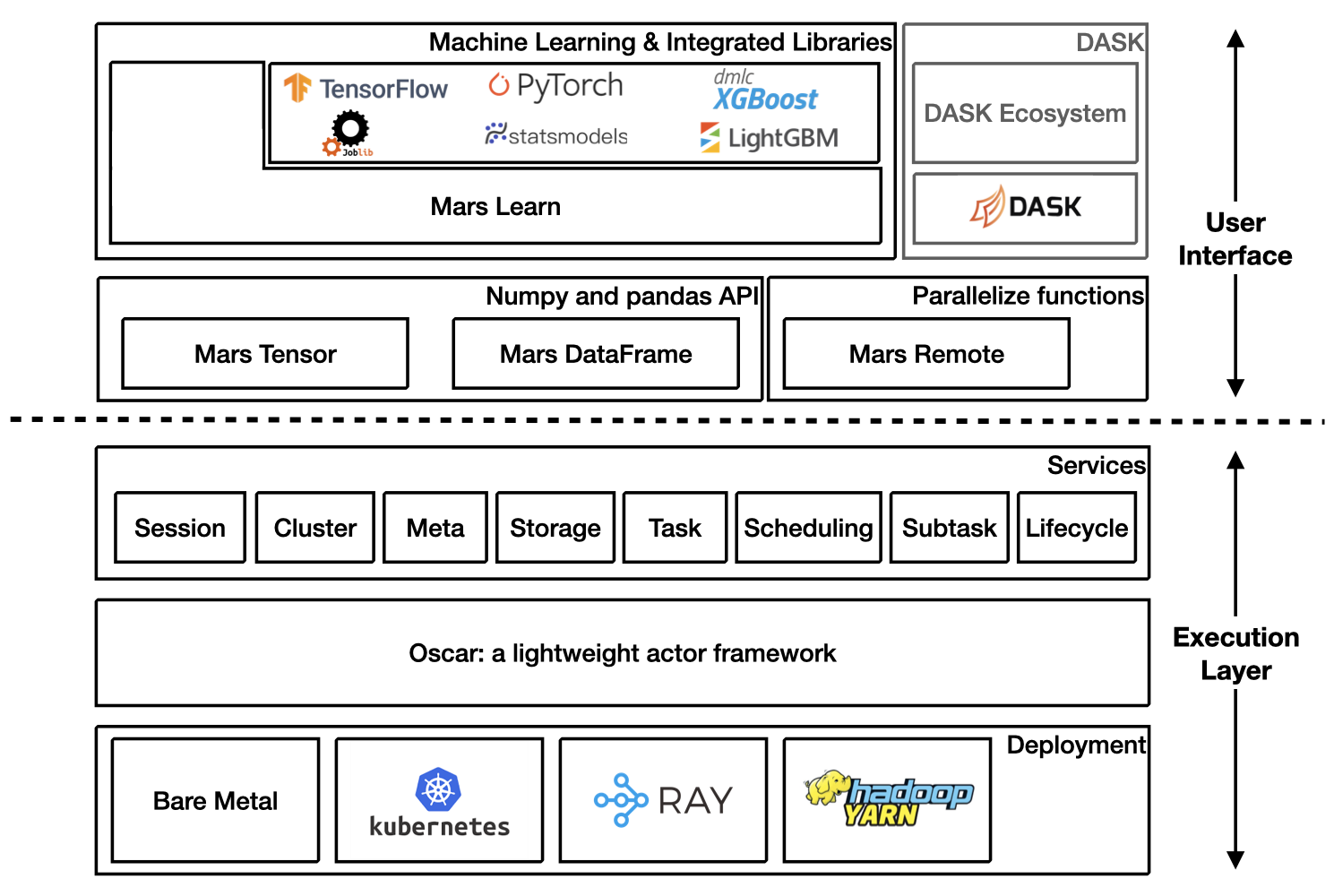
Mars is a tensor-based unified framework for large-scale data computation which scales numpy, pandas, scikit-learn and many other libraries.
Documentation,Tiếng Trung hồ sơ
Mars is easy to install by
pip install pymarsWhen you want to contribute code to Mars, you can follow the instructions below to install Mars for development:
git clone https://github /mars-project/mars.git
cdmars
pip install -e".[dev]"More details about installing Mars can be found at installationsection in Mars document.
Starting a new runtime locally via:
>>>importmars
>>>mars.new_session()Or connecting to a Mars cluster which is already initialized.
>>>importmars
>>>mars.new_session('http://<web_ip>:<ui_port>')Mars tensor provides a familiar interface like Numpy.
| Numpy | Mars tensor |
importnumpyasnp
N=200_000_000
a=np.random.uniform(-1,1,size=(N,2))
print((np.linalg.norm(a,axis=1)<1)
.sum()*4/N) |
importmars.tensorasmt
N=200_000_000
a=mt.random.uniform(-1,1,size=(N,2))
print(((mt.linalg.norm(a,axis=1)<1)
.sum()*4/N).execute()) |
3.14174502
CPU times: user 11.6 s, sys: 8.22 s,
total: 19.9 s
Wall time: 22.5 s
|
3.14161908
CPU times: user 966 ms, sys: 544 ms,
total: 1.51 s
Wall time: 3.77 s
|
Mars can leverage multiple cores, even on a laptop, and could be even faster for a distributed setting.
Mars DataFrame provides a familiar interface like pandas.
| Pandas | Mars DataFrame |
importnumpyasnp
importpandasaspd
df=pd.DataFrame(
np.random.rand(100000000,4),
columns=list('abcd'))
print(df.sum()) |
importmars.tensorasmt
importmars.dataframeasmd
df=md.DataFrame(
mt.random.rand(100000000,4),
columns=list('abcd'))
print(df.sum().execute()) |
CPU times: user 10.9 s, sys: 2.69 s,
total: 13.6 s
Wall time: 11 s
|
CPU times: user 1.21 s, sys: 212 ms,
total: 1.42 s
Wall time: 2.75 s
|
Mars learn provides a familiar interface like scikit-learn.
| Scikit-learn | Mars learn |
fromsklearn.datasetsimportmake_blobs
fromsklearn.decompositionimportPCA
X,y=make_blobs(
n_samples=100000000,n_features=3,
centers=[[3,3,3], [0,0,0],
[1,1,1], [2,2,2]],
cluster_std=[0.2,0.1,0.2,0.2],
random_state=9)
pca=PCA(n_components=3)
pca.fit(X)
print(pca.explained_variance_ratio_)
print(pca.explained_variance_) |
frommars.learn.datasetsimportmake_blobs
frommars.learn.decompositionimportPCA
X,y=make_blobs(
n_samples=100000000,n_features=3,
centers=[[3,3,3], [0,0,0],
[1,1,1], [2,2,2]],
cluster_std=[0.2,0.1,0.2,0.2],
random_state=9)
pca=PCA(n_components=3)
pca.fit(X)
print(pca.explained_variance_ratio_)
print(pca.explained_variance_) |
Mars learn also integrates with many libraries:
Mars remote allows users to execute functions in parallel.
| Vanilla function calls | Mars remote |
importnumpyasnp
defcalc_chunk(n,i):
rs=np.random.RandomState(i)
a=rs.uniform(-1,1,size=(n,2))
d=np.linalg.norm(a,axis=1)
return(d<1).sum()
defcalc_pi(fs,N):
returnsum(fs)*4/N
N=200_000_000
n=10_000_000
fs=[calc_chunk(n,i)
foriinrange(N//n)]
pi=calc_pi(fs,N)
print(pi) |
importnumpyasnp
importmars.remoteasmr
defcalc_chunk(n,i):
rs=np.random.RandomState(i)
a=rs.uniform(-1,1,size=(n,2))
d=np.linalg.norm(a,axis=1)
return(d<1).sum()
defcalc_pi(fs,N):
returnsum(fs)*4/N
N=200_000_000
n=10_000_000
fs=[mr.spawn(calc_chunk,args=(n,i))
foriinrange(N//n)]
pi=mr.spawn(calc_pi,args=(fs,N))
print(pi.execute().fetch()) |
3.1416312
CPU times: user 32.2 s, sys: 4.86 s,
total: 37.1 s
Wall time: 12.4 s
|
3.1416312
CPU times: user 616 ms, sys: 307 ms,
total: 923 ms
Wall time: 3.99 s
|
Refer toDASK on Marsfor more information.
Mars supports eager mode which makes it friendly for developing and easy to debug.
Users can enable the eager mode by options, set options at the beginning of the program or console session.
>>>frommars.configimportoptions
>>>options.eager_mode=TrueOr use a context.
>>>frommars.configimportoption_context
>>>withoption_context()asoptions:
>>>options.eager_mode=True
>>># the eager mode is on only for the with statement
>>>...If eager mode is on, tensor, DataFrame etc will be executed immediately by default session once it is created.
>>>importmars.tensorasmt
>>>importmars.dataframeasmd
>>>frommars.configimportoptions
>>>options.eager_mode=True
>>>t=mt.arange(6).reshape((2,3))
>>>t
array([[0,1,2],
[3,4,5]])
>>>df=md.DataFrame(t)
>>>df.sum()
03
15
27
dtype:int64Mars also has deep integration with Ray and can run onRayefficiently and interact with the large ecosystem of machine learning and distributed systems built on top of the core Ray.
Starting a new Mars on Ray runtime locally via:
importmars
mars.new_session(backend='ray')
# Perform computationInteract with Ray Dataset:
importmars.tensorasmt
importmars.dataframeasmd
df=md.DataFrame(
mt.random.rand(1000_0000,4),
columns=list('abcd'))
# Convert mars dataframe to ray dataset
ds=md.to_ray_dataset(df)
print(ds.schema(),ds.count())
ds.filter(lambdarow:row["a"]>0.5).show(5)
# Convert ray dataset to mars dataframe
df2=md.read_ray_dataset(ds)
print(df2.head(5).execute())Refer toMars on Rayfor more information.
Mars can scale in to a single machine, and scale out to a cluster with thousands of machines. It's fairly simple to migrate from a single machine to a cluster to process more data or gain a better performance.
Mars is easy to scale out to a cluster by starting different components of mars distributed runtime on different machines in the cluster.
A node can be selected as supervisor which integrated a web service, leaving other nodes as workers. The supervisor can be started with the following command:
mars-supervisor -h<host_name>-p<supervisor_port>-w<web_port>Workers can be started with the following command:
mars-worker -h<host_name>-p<worker_port>-s<supervisor_endpoint>After all mars processes are started, users can run
>>>sess=new_session('http://<web_ip>:<ui_port>')
>>># perform computationRefer toRun on Kubernetesfor more information.
Refer toRun on Yarnfor more information.
- Readdevelopment guide.
- Join our Slack workgroup:Slack.
- Join the mailing list: send an email tomars-dev@googlegroups.
- Please report bugs by submitting aGitHub issue.
- Submit contributions usingpull requests.
Thank you in advance for your contributions!