ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥି
| Parathyroid glands | |
|---|---|

| |
| Diagram showing structures in thehuman neck.The four green shaded areas represent the most common position of the parathyroid glands, which are generally four in number and situated behind the lateral lobes of thethyroid gland(shaded orange). | |

| |
| Thyroid and parathyroids as viewed from the back of the neck | |
| ଲାଟିନ ଭାଷାରେ | glandula parathyreoidea inferior, glandula parathyreoidea superior |
| ବିଭାଗ | Endocrine |
| ଧମନୀ | superior thyroid artery,inferior thyroid artery, |
| ଶିରା | superior thyroid vein,middle thyroid vein,inferior thyroid vein, |
| ସ୍ନାୟୁ | middle cervical ganglion,inferior cervical ganglion |
| ଲସିକା | pretracheal,prelaryngeal,jugulodigastric lymph nodes |
| Precursor | neural crestmesenchymeand third and fourthpharyngeal pouchendoderm |
ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିକହିଲେ ମାନବ ଓ ଚତୁଷ୍ପଦ ପ୍ରାଣୀଙ୍କ ଦେହରେ ଥିବା ଛୋଟ ଛୋଟଅନ୍ତସ୍ରାବୀ(endocrine) ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିମାନଙ୍କୁ ବୁଝାଏ । ମାନବ ଦେହରେ ଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥି ପୃଷ୍ଠଭାଗରେ ଚାରୋଟି ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥି ଥାଏ । ରକ୍ତରେ ସ୍ୱଳ୍ପ କ୍ୟାଲସିଅମ ଥିଲେ ଏହି ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିଗୁଡ଼ିକପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ହରମୋନ(parathyroid hormone) ପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ ଓ କ୍ଷରଣ କରନ୍ତି ଓ ଏହି ହରମୋନ ଶରୀରରେ ଓ ଅସ୍ଥି ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଥିବା କ୍ୟାଲସିଅମ ପରିମାଣକୁ ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରଣ କରେ ।
ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିର ରକ୍ତ, ଧମନୀ, ଶିରା ଓ ଲସିକା ସରବରାହ ଠିକ୍ ଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିର ସରବରାହ ଭଳି ହୋଇଥାଏ । ଭୃଣ ବିଜ୍ଞାନ ଅନୁସାରେ ତୃତୀୟ ଓ ଚତୁର୍ଥ ଫାରିଞ୍ଜିଆଲ ପାଉଚର (pharyngeal pouches) ଏପିଥେଲିଆଲ (epithelial) ଲାଇନିଙ୍ଗରୁ ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥି ସୃଷ୍ଟି ହୋଇଥାଏ; ଉପର ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଚତୁର୍ଥ ପାଉଚରୁ ଓ ତଳ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିଗୁଡ଼ିକ ତୃତୀୟ ପାଉଚରୁ ତିଆରି ହୋଇଥାଏ ।
ଅଧିକ ବା କମ୍ ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ହରମୋନ ଅନୁସାରେ ରକ୍ତରକ୍ୟାଲସିଅମସ୍ତର ଓ ଅସ୍ଥି ମେଟାବୋଲିଜ୍ମର ପରିବର୍ତ୍ତନ ହୁଏ ଯାହାକୁ ଯଥାକ୍ରମେହାଇପରପାରାଥାଇରଏଡିଜ୍ମଓହାଇପୋପାରାଥାଇରଏଡିଜ୍ମ(hypoparathyroidism) କୁହାଯାଏ ।
ଗଠନ[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]
ବାମ ଓ ଡାହାଣଥାଇରଏଡଗ୍ରନ୍ଥି ଲୋବର ପୃଷ୍ଠ ଭାଗରେ ଦୁଇ ଯୋଡ଼ା ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥି ଥାଏ । ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିର ରଙ୍ଗ ହଳଦିଆ-ମାଟିଆ, ଦେଖିବାକୁ ଅଣ୍ଡାକୃତି ଚଟକା ଓ ମସୁର ଭଳି ଦେଖିବାକୁ, ଲମ୍ବ ୬ ମି:ମି: ଓ ଚଉଡ଼ା ୩ ମି:ମି: ।[୧]ସ୍ୱାଭାବିକ ଭାବରେ ଚାରୋଟି ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥି ଥାଏ; ଉପର ପାଖରେ ଦୁଇ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିକୁ ସୁପିରିଅର ଓ ତଳ ପାଖର ଦୁଇ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିକୁ ଇନଫିରିଅର ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥି କୁହାଯାଏ । ସୁସ୍ଥ ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିର ଓଜନ ପୁରୁଷଙ୍କର ୩୦ମି:ଗ୍ରା: ଓ ମହିଳାଙ୍କର ୩୫ମି:ଗ୍ର: ହୋଇଥାଏ ।[୨]ଏହି ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଦେଖାଯାଏ ନାହିଁ ବା ବେକ ପରୀକ୍ଷା କରି ଜାଣିହୁଏ ନାହିଁ ।[୩]
ପ୍ରତ୍ୟେକ ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ଶିରା ଯାଇ ସୁପିରିଅର, ମିଡଲ ଓ ଇନଫିରିଅର ଥାଇରଏଡ ଶିରା ସହିତ ମିଳିତ ହୁଏ । ସୁପିରିଅର ଓ ମିଡଲ ଥାଇରଏଡ ଶିରା ଯାଇ ଇଣ୍ଟରନାଲ ଜୁଗୁଲାର ଶିରା ((internal jugular vein) ସହିତ ଓ ଇନଫିରିଅର ଥାଇରଏଡ ଯାଇ ବ୍ରାକିଓସେଫାଲିକ ଶିରା (brachiocephalic vein) ସହିତ ସଂଯୁକ୍ତ ହୋଇଥାଏ ।[୪]
ଲସିକା ନିଷ୍କାସନ[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]
ଲସିକା ନଳୀଗୁଡ଼ିକ ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିରୁ ବାହାରି ଡିପ ସର୍ଭିକାଲ ଲିମ୍ଫ ନୋଡ (deep cervical lymph node) ଓ ପାରାଟ୍ରାକିଆଲ ଲିମ୍ଫ ନୋଡମାନଙ୍କରେ (paratracheal lymph nodes) ଲସିକା ନିଷ୍କାସନ ହୁଏ ।[୪]
ଉତ୍ତକ ବିଜ୍ଞାନ/ Histology[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]
ଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥି ପାଖରେ ଥିବାରୁ ଏହାର ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ନାମକରଣ ହୋଇଛି କିନ୍ତୁ ଏହାର କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଥାଇରଏଡଠାରୁ ସମ୍ପୁର୍ଣ୍ଣ ପୃଥକ୍ । ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡର ଜୀବକୋଷଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଘଞ୍ଚ ଭାବରେ ଲଗାଲଗି ହୋଇ ଥାଆନ୍ତି କିନ୍ତୁଥାଇରଏଡଜୀବକୋଷର ଫଲିକୁଲାର ଗଠନ ଥାଏ ।[୫]ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡର ଦୁଇ ପ୍ରକାର ଅତୁଳନୀୟ ଜୀବକୋଷ ଥାଏ ।
- ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ମୁଖ୍ୟ ଜୀବକୋଷChief cellsଗୁଡ଼ିକ ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ହରମୋନ ତିଆରି ଓ ନିଷ୍କାସନ କରନ୍ତି । ଜୀବକୋଷଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଛୋଟ ଓ ହରମୋନ ଥିବା ବେଳେ କଳା, ହରମୋନ ନିଷ୍କାସିତ ହୋଇଥିବା ବେଳେ ପରିସ୍କାର ଦେଖାଯାଆନ୍ତି ।[୬]
- ଅକ୍ସିଫିଲ ଜୀବକୋଷ/Oxyphil cellsଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଦେଖିବାକୁ ଫିକା ଓ ବୟସ ବୃଦ୍ଧି ସାଥିରେ ଏମାନେ ସଂଖାଧିକ ହୁଅନ୍ତି,[୬]କର୍ମ ଅଧ୍ୟବଧି ଅଜ୍ଞାତ ଅଛି ।[୭]
-
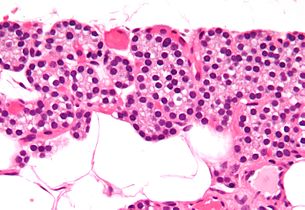
Intermediate magnificationmicrograph.H&E stain.ଧଳା ଗୋଲ ପଦାର୍ଥ ଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଚର୍ବି ଜୀବକୋଷ । ସାଧାରଣ ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିରେ ଆଡିପୋଜ ତନ୍ତୁ ପ୍ରାୟ ୨୫-୪୦% ଆଡିପୋଜ ତନ୍ତୁ ଥାଏ ।[୬]
-
High magnificationmicrograph.H&E stain.ଛୋଟ ଗାଢ଼ କୋଷ ଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଚିଫ ଜୀବକୋଷ ।
-
High magnificationmicrograph.H&E stain.The cells with orange/pink staining cytoplasm areoxyphil cells
କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]
ଶରୀରରେ ଥିବାକ୍ୟାଲସିଅମଓ ଫସଫେଟକୁ (phosphate) ସୀମିତ ସ୍ତରରେ ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରଣ କରି ରଖିବା ଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିର ମୂଖ୍ୟ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ଯାହା ଫଳରେ ସ୍ନାୟୁ ମଣ୍ଡଳ (nervous) ଓ ମାଂସପେଶୀ ମଣ୍ଡଳ (muscular system) ସଠିକ ଭାବରେ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟକ୍ଷମ ହୋଇପାରିବେ । ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ହରମୋନ (parathyroid hormone/ PTH) କ୍ଷରଣ କରି ଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥି ଏହି କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ସମ୍ପାଦନ କରେ ।[୮]
ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ହରମୋନ ଏକ ଛୋଟ ପ୍ରୋଟିନ (protein) ଯାହା କ୍ୟାଲସିଅମ ତଥା ଫସଫେଟ ସମତୁଲ ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରଣ କରିବାରେ ଓ ଅସ୍ଥି ଶରୀରତତ୍ତ୍ୱରେ ଭାଗ ନିଏ । କ୍ୟାଲସିଟୋନିନcalcitoninପ୍ରତିପକ୍ଷ ହୋଇ ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ହରମୋନ କାମ କରେ ।[୯]
ଆଧାର[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]
- ↑Gray, Henry(1980). Williams, Peter L; Warwick, Roger (eds.).Gray's Anatomy(36th ed.).Churchill Livingstone.p. 1453.ISBN0-443-01505-8.
- ↑Johnson, S J (1 April 2005)."Best Practice No 183: Examination of parathyroid gland specimens".Journal of Clinical Pathology.58(4): 338–342.doi:10.1136/jcp.2002.002550.PMC1770637.PMID15790694.
- ↑Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 159
- ↑୪.୦୪.୧Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005).Gray's anatomy for students.Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. p. 918.ISBN978-0-8089-2306-0.
- ↑Lappas D, Noussios G, Anagnostis P, Adamidou F, Chatzigeorgiou A, Skandalakis P (September 2012). "Location, number and morphology of parathyroid glands: results from a large anatomical series".Anat Sci Int.87(3): 160–4.doi:10.1007/s12565-012-0142-1.PMID22689148.
- ↑୬.୦୬.୧୬.୨Young, Barbara; Heath, John W.; Stevens, Alan; Burkitt, H. George (2006).Wheater's functional histology: a text and colour atlas(5th ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. p. 337.ISBN978-0-443-06850-8.
- ↑Ritter, Cynthia S.; Haughey, Bruce H.; Miller, Brent; Brown, Alex J. (August 2012)."Differential Gene Expression by Oxyphil and Chief Cells of Human Parathyroid Glands".The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.97(8): E1499–E1505.doi:10.1210/jc.2011-3366.PMC3591682.PMID22585091.
- ↑Young, Barbara; Heath, John W.; Stevens, Alan; Burkitt, H. George (2006).Wheater's functional histology: a text and colour atlas(5th ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. p. 336.ISBN978-0-443-06850-8.
- ↑Hall, Arthur C. Guyton, John E. (2005).Textbook of medical physiology(11th ed.). Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders. pp. 985–8.ISBN978-0-7216-0240-0.
{{cite book}}:CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)

![Intermediate magnification micrograph. H&E stain. ଧଳା ଗୋଲ ପଦାର୍ଥ ଗୁଡ଼ିକ ଚର୍ବି ଜୀବକୋଷ । ସାଧାରଣ ପାରାଥାଇରଏଡ ଗ୍ରନ୍ଥିରେ ଆଡିପୋଜ ତନ୍ତୁ ପ୍ରାୟ ୨୫-୪୦% ଆଡିପୋଜ ତନ୍ତୁ ଥାଏ । [୬]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4a/Parathyroid_gland_intermed_mag.jpg/315px-Parathyroid_gland_intermed_mag.jpg)