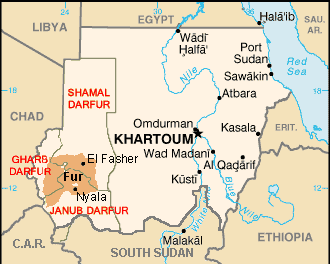
Darfur

Darfur(Arabicدار فور, meaning "home of theFur") is a region of far westernSudan.
It borders theCentral African Republic,Libya,andChad.It is divided into three federal states withinSudan:Gharb Darfur (West Darfur), Janub Darfur (South Darfur), and Shamal Darfur (North Darfur). Since 2003 there has been an ongoinghumanitariancrisis that developed from the conflict betweenGanjaweedmilitias and theSudan Liberation MovementandJustice and Equality Movement.
Geography and climate[change|change source]

Darfur covers an area of about 493 180 km² (196,555 miles²)—just over two-thirds the size ofFranceand more than half the size ofKenya.It is largely anaridplateau with theMarrah Mountains(Jebel Marra), a range of volcanic peaks rising up to 3000 m (10,100 ft), in the center. The region's main towns areAl Fashir,Nyala,andGeneina.
There are four main features of the physical geography. The whole eastern half of Darfur is covered with plains and low hills of sandy soils, known asgoz,andsandstonehills. In many places thegozis waterless and can only be inhabited where there are water reservoirs or deepboreholes.To the north thegozis overtaken by the desert sands of theSahara.A second feature are thewadis,seasonal watercourses ranging from small rivulets that flood only occasionally during the wet season to largewadisthat flood for most of the rains and flow from western Darfur hundreds of miles west toLake Chad.Manywadishave pans ofalluviumwith rich soil that are also difficult to cultivate. The west of Darfur is dominated by the third feature,basement rock,sometimes covered with a thin layer of sandy soil. Basement rock is too infertile to be farmed, but provides some forest cover that can be grazed by animals. The fourth and final feature is theMarrah Mountains,that rise up to a peak atDeriba craterwhere there is a small area of temperate climate, high rainfall and permanent springs of water.
The rainy season is from June through September, transforming much of the region from dusty brown to green. Because much of the population of Darfur is agricultural, the rains are vital. In normal years, a crop is ready to be harvested by November. Once harvested, the dry stalks may be fed to domestic livestock. In the far northern desert, years may pass between rainfall. In the far south, annual average rainfall is 700 mm and many trees remain green year-round.[1]
Economy and demography[change|change source]
Darfur has a population of about 7.4 million people. Darfur's economy is primarily based onsubsistence agriculture,producingcereals,fruitandtobaccoas well aslivestockin the drier north. Darfur suffers from frequentdroughts during the summer and heavy rainfall in the winter.[2]This has caused many farmers to provide inadequate crops causing the deaths of thousands of people.
Darfur Conflict[change|change source]
The Darfur conflict is an ongoing armed conflict between theJanjaweedmilitia group and the tribes of the region. The United Nations estimates that over 400,000 people have died since the beginning of this conflict.[3]
Related pages[change|change source]
Notes and references[change|change source]
- ↑de Waal, Alex,Famine that Kills: Darfur, Sudan,Oxford University Press(Revised edition), 2005,ISBN0-19-518163-8,p. 36
- ↑[1]Archived2011-02-24 at theWayback MachineDarfur
- ↑[2]United Nations
Other websites[change|change source]
- Pulitzer Center on Crisis ReportingArchived2007-09-28 at theWayback Machine"Our Choice, Too: On the Edge in Darfur" (Video)
- African Holocaust Darfur ReportArchived2007-03-24 at theWayback Machine
- "Delivering Aid to Darfur" (with video) about AmeriCares efforts in DarfurArchived2007-07-11 at theWayback Machine
- Safer Access -A Collective Response on Darfur is NeededArchived2015-10-17 at theWayback Machine
