Heart
Theheartis anorganfound in everyvertebrate.It is a very strong muscle. It is on the left side of the body in humans and is about the size of a fist. It pumpsbloodthroughout thebody.It has regularcontractions,or when the heart squeezes the blood out into other parts of the body.
Cardiacandcardioboth mean "about the heart", so if something has theprefixcardioorcardiac,it has something to do with the heart.
Myocardiummeans the heart muscle: 'myo' is from theGreekword for muscle - 'mys', cardium is from theGreekword for heart - 'kardia'.
Structure[change|change source]
The human heart has fourchambersor closed spaces. Some animals have only two or three chambers.
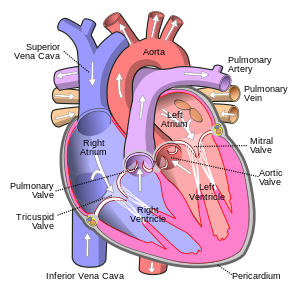
In humans, the four chambers are twoatriaand twoventricles.Atria is talking about two chambers; atrium is talking about one chamber. There is a right atrium and right ventricle. These get blood that comes to the heart. They pump this blood to thelungs.In the lungs blood picks upoxygenand dropscarbon dioxide.Blood from the lungs goes to the left atrium and ventricle. The left atrium and ventricle send the blood out to the body. The left ventricle works six times harder than the right ventricle because it carries oxygenated blood.[1]
Blood is carried inblood vessels.These arearteriesandveins.Blood going to the heart is carried in veins. Blood going away from the heart is carried in arteries. The main artery going out of the right ventricle is thepulmonary artery.(Pulmonary means about lungs.) The main artery going out of the left ventricle is theaorta.
The veins going into the right atrium are thesuperior vena cavaandinferior vena cava.These bring blood from the body to the right heart. The veins going into the left atrium are thepulmonary veins.These bring blood from the lungs to the left heart.
When the blood goes from the atria to the ventricles it goes through heartvalves.When blood goes out of the ventricles it goes through valves. The valves make sure that blood only goes one way in or out.
The four valves of the heart are:
- Atria to ventricle valves
- Tricuspid valve– blood goes from right atrium to right ventricle
- Mitral valve– blood goes from left atrium to left ventricle
- Ventricles to arteries
- Pulmonic valve– blood goes out of the right ventricle to the lungs (through thepulmonic artery)
- Aortic valve– blood goes out of the left ventricle to the body (through theaorta)
The heart has three layers. The outer covering is thepericardium.This is a tough sack that surrounds the heart. The middle layer is themyocardium.This is the heart muscle. The inner layer is theendocardium.This is the thin smooth lining of the chambers of the heart.[2]
Cardiac cycle[change|change source]
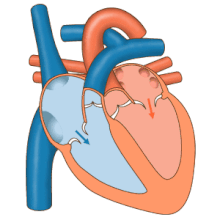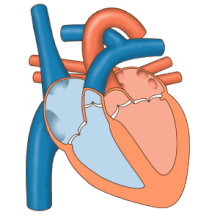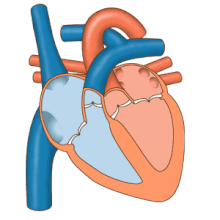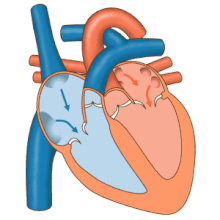
Aheart beatis when the heart musclecontracts.This means the heart pushes in and this makes the chambers smaller. This pushes blood out of the heart and into the blood vessels. After the heart contracts and pushes in, the musclerelaxesor stops pushing in. The chambers get bigger and blood coming back to the heart fills them.
When the heart muscle contracts (pushes in) it is calledsystole.When the heart muscle relaxes (stops pushing in), this is calleddiastole.Both atria do systole together. Both ventricles do systole together. But the atria do systolebeforethe ventricles. Even though theatrial systolecomes beforeventricular systole,all four chambers do diastole at the same time. This is calledcardiac diastole
The order is: atrial systole → ventricular systole → cardiac diastole. When this happens one time, it is called acardiac cycle.
Heart's pacemaker[change|change source]
Systole (when the heart squeezes) happens because the musclecellsof the heart gets smaller in size. When they get smaller we also say theycontract.Electricitygoing through the heart makes the cells contract. The electricity starts in thesino-atrial node(acronymSA Node) The SA Node is a group of cells called pacemaker cells in the right atria. These cells start anelectrical impulse.This electrical impulse sets the rate and timing at which all cardiac muscle cells contract. This motion is called 'atrial systole'. Once electrical impulse goes through theatrio-ventricular node(AV Node). The AV Node makes the impulse slow down. Slowing down makes the electrical impulses get to the ventricles later. That is what makes the ventricular systole occurafteratrial systole, and lets all the blood leave the atria before ventricle contracts (meaning squeeze).
After the electrical impulse goes through the AV Node, the electrical impulse will go through theconduction systemof the ventricle.Conductionmeansheator electricity traveling through something. This brings the electrical impulse to the ventricles. The first part of the conduction system is thebundle of His.Hisis named for the doctor (Wilhelm His, Jr) who discovered it. Bundle means strings or wires grouped together in parallel. Once the bundle (meaning a group of strings or wires going in parallel directions) goes through the ventricle muscle, it divides into twobundle branches,the left bundle branch and the right bundle branch. The left bundle branch travels to the left ventricle and the right bundle branch travels to the right ventricle. At the end of the bundle branches, the electrical impulse goes into the ventricular muscle through thePurkinje Fibers.This is what makes ventricle contraction take place and makes ventricular systole.
The order is: Sino-Atrial Node → Atria (systole) → Atrio-Ventricular Node → Bundle of His → Bundle branches →Purkinje Fibers→ Ventricles (systole)
ECG[change|change source]
ECG is anacronymforElectroCardioGram. It is also written EKG forElectroKardioGram inGerman.The ECG shows what the electricity in the heart is doing. An ECG is done by puttingelectrodeson a person's skin. The electrodes see the electricity going through the heart. This is written on paper by amachine.This writing on the paper is the ECG.
Doctorslearn about the person's heart by looking at the ECG. The ECG shows some diseases of the heart likeheart attacksor problems with therhythmof the heart (how the electricity goes through the heart's conduction system.)
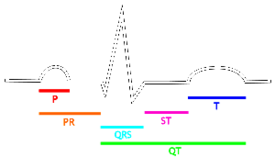
The ECG shows atrial systole. This is called aP-wave.Then ventricular systole happens. This is called theQRSor QRS-complex. It is called a complex because there are three different waves in it. The Q-wave, R-wave, and S-wave. Then the ECG shows ventricular diastole. This is called theT-wave.Atrial diastole happens then too. But it is not seen separate from ventricular diastole.
ThePR-Intervalis the space between atrial systole (P) and ventricular systole (QRS). TheQT-Intervalis from when the QRS starts to when the T ends. TheST-segmentis the space between the QRS and T.

References[change|change source]
- ↑Phibbs, Brendan (2007).The human heart: a basic guide to heart disease(2nd ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p.1.ISBN9780781767774.
- ↑Betts, J. Gordon (2013).Anatomy & physiology.ISBN978-1938168130.Retrieved11 August2014.
Other websites[change|change source]
- Symptoms ofheart disease
- What is the heart?- NIH
- The gross physiology of the cardiovascular system (2nd Ed., 2012)– Robert M. Anderson, M.D. (CC-BY-NC)
- Atlas of human cardiac anatomy
- "healthy heart" Blog
