Myanmar
Republic of the Union of Myanmar ပြည်ထောင်စု သမ္မတ မြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော် | |
|---|---|
| Anthem:Kaba Ma Kyei Till the End of the World | |
![Location of Myanmar (green) in ASEAN (dark grey) — [Legend]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b8/Location_Burma_%28Myanmar%29_ASEAN.svg/250px-Location_Burma_%28Myanmar%29_ASEAN.svg.png) | |
| Capital | Naypyidawa 19°45′N96°6′E/ 19.750°N 96.100°E |
| Largest city | Yangon(Rangoon) |
| Official languages | Burmese |
| Recognised national languages | English |
| Recognised regional languages | |
| Official scripts | Burmese script |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Demonym(s) | Burmese / Myanma |
| Government | Unitarypresidentialconstitutionalrepublic |
| Myint Swe(acting) | |
|
Other members | |
| Legislature | Assembly of the Union |
| House of Nationalities | |
| House of Representatives | |
| Formation | |
| 23 December 849 | |
| 16 October 1510 | |
| 29 February 1752 | |
•Independence (fromUnited Kingdom) | 4 January 1948 |
| 2 March 1962 | |
| 30 March 2011 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 676,578 km2(261,228 sq mi) (40th) |
• Water (%) | 3.06 |
| Population | |
• 2010 estimate | 60,280,000[1](24th[2]) |
• 1983 census | 33,234,000 |
• Density | 73.9/km2(191.4/sq mi) (119th) |
| GDP(PPP) | 2012 estimate |
• Total | $89.461 billion[3] |
• Per capita | $1,405[3] |
| GDP(nominal) | 2012 estimate |
• Total | $53.140 billion[3] |
• Per capita | $854[3] |
| HDI(2012) | low·149th |
| Currency | Kyat(K) (MMK) |
| Time zone | UTC+06:30(MST) |
| Driving side | rightb |
| Calling code | +95 |
| ISO 3166 code | MM |
| Internet TLD | .mm |
| |
Myanmaris a country inSoutheast Asia.Its full name is theRepublic of the Union of Myanmar.It used to be calledBurma.Myanmar is a country in Southeast Asia that is not an island. It is also part ofSouth Asia.
It is bordered byChinaon the north,Laoson the east,Thailandon the southeast,Bangladeshon the west, andIndiaon the northwest, with theAndaman Seato the south, and theBay of Bengalto the southwest. There are over 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) of coastline.
Government[change|change source]
The country was ruled by amilitaryjuntaled byGeneralNe Winfrom 1962 to 1988. Its political system today stays under the tight control of its military government. In 1991, Senior GeneralThan Shwebegan ruling the country. In 2011Thein Seinwas elected as a first president of the civilian government. In 2016Htin Kyawbecame the second elected civilian leader.[6]Aung San Suu Kyi,who is prevented from becoming president by theconstitutionof Myanmar, will act as an advisor to Kyaw.[6]
In March 2018,Win Myintbecame the country's tenth and current President.
Since 2021, Myanmar is again ruled by a Junta.
Origin and history of the name[change|change source]
In 1989, the military junta officially changed theEnglishversion of its name fromBurmatoMyanmar.It also made a new name in English for places in the country, such as its formercapital city,fromRangoontoYangon.The official name of the country in theBurmese language,Myanmardid not change, however. The renaming was controversial, seen by some aslinguisticallybad. Accepting the name change in the English-speaking world has been slow, with many people still using the nameBurmato refer to the country. Major news organizations like theBBCstill call it Burma. Some question the military junta's authority to "officially" change the name in English in the first place.Aung San Suu Kyi,however, calls the country Myanmar now.
History[change|change source]
Myanmar had a strong kingdom in ancient times, but the nation was taken over by theBritishin the 1800s. It was occupied by theEmpire of Japanin the 1940s. Myanmar became independent in 1948 as the Union of Burma, and had a democratic government at first. However, in 1962, acoup d'étatbrought the military into power, where it has been ever since. The founder of modern Myanmar,Aung Sanwas assassinated months before independence. His daughterAung San Suu Kyiwas placed under house arrest many times for leading the democracy movement.
In 1991, the military junta agreed to democratic elections, which were won by theNational League for Democracy,and should have made Aung San Suu Kyi the Prime Minister. However, the dictatorship ignored the results of the elections and continued ruling. InNovember2005, the militarygovernmentstated that the national capital would be moved fromYangonto a location nearPyinmana,which was renamedNaypyidawinMarch2006.
Since independence in 1948 and the assassination of Aung San, Burma has hadcivil warsbetween its governments and minorityethnic groupslike theKachin,Karen,Shanand others. These conflicts are known as theInternal conflict in Burma.
National symbols of Myanmar[change|change source]
-
National animal of Myanmar
-
National bird of Myanmar
-
National flower of Myanmar
-
Irrawaddy Dolphin
Land[change|change source]
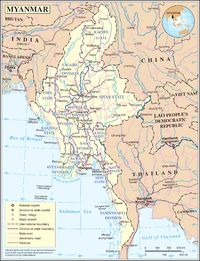
Today, there are 14 sections. 7 are calledstatesand the other 7 are calleddivisions.
The divisions are split intotownships.The townships are divided intovillagesand wards.
Largest cities[change|change source]
Photos[change|change source]
Related pages[change|change source]
References[change|change source]
- ↑"Asian Development Bank and Myanmar: Fact Sheet".Asian Development Bank. 30 April 2012. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 2018-12-26.Retrieved2012-11-20.
- ↑"The World Factbook".Cia.gov. Archived fromthe originalon 2018-08-10.Retrieved2013-07-06.
- ↑3.03.13.23.3"Burma (Myanmar)".International Monetary Fund.Retrieved1 April2013.
- ↑"2013 Human Development Report Statistics"(PDF).Human Development Report 2013.United Nations Development Programme. 14 March 2013. Archived fromthe original(PDF)on 19 March 2013.Retrieved16 March2013.
- ↑"The World Factbook – Burma".cia.gov. Archived fromthe originalon 17 January 2018.Retrieved1 September2012.
- ↑6.06.1"Myanmar swears in first elected civilian president in 50 years".BBC. 30 March 2016.Retrieved30 October2016.













