Somme River
| Somme | |
|---|---|
 The Somme | |
 Course in Northern France | |
| Location | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Picardy |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| - location | Fonsommes |
| - coordinates | 49°54′23″N03°24′11″E/ 49.90639°N 3.40306°E |
| - elevation | 85 m (279 ft) |
| Mouth | |
| - location | Saint-Valery-sur-Somme English Channel |
| - coordinates | 50°11′10″N01°38′35″E/ 50.18611°N 1.64306°E |
| Length | 245 km (152 mi) |
| Basin size | 6,550 km2(2,530 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| - location | Abbeville |
| - average | 35 m3/s (1,200 cu ft/s) |
TheSommeis ariverin the north ofFrance,in theHauts-de-Franceregion,and gives its name to the department calledSomme.
The name of the river is ofCelticorigins, and refers to the tranquility of the river over much of its course. The river is known for theBattle of the Somme,which was an important battle of theFirst World War.
Geography
[change|change source]The Somme river has a length of 245 km (152.2 mi),[1]and adrainage basinwith an area of 6,550 km2(2,529 sq mi).
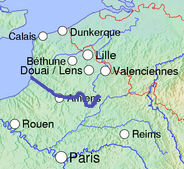
Course
[change|change source]
Thesourceof the Somme is in theFonsommecommune(Aisne), at analtitudeof about 86 m (282 ft).[2]
The Somme passes through the departments and cities of:
The Somme river flows through 49communes.[3]
Finally, it flows into theEnglish ChannelnearSaint-Valery-sur-Somme.[4]
Main tributaries
[change|change source]- Left tributaries
- Right tributaries
Archaeology
[change|change source]Differentarcheologicalfinds have been discovered in its valley: TheAcheuleanculture is named after Saint-Acheul, asuburbof Amiens.Hand axesfrom thePalaeolithicperiod were found there, and gave this name to the respective period.
Related pages
[change|change source]References
[change|change source]- ↑"Eaux superficielles et souterraines"(in French). AMEVA.org.Retrieved12 June2016.
- ↑"Source de la Somme"(in French). Géoportail.Retrieved12 June2016.
- ↑"La Somme Rivière (E6---140)"(in French). SANDRE - Portail national d'accès aux référentiels sur l'eau. Archived fromthe originalon 3 March 2016.Retrieved12 June2016.
- ↑"Confluence de la Somme"(in French). Géoportail.Retrieved12 June2016.
- ↑"Avre (E6400600)"(in French). SANDRE - Portail national d'accès aux référentiels sur l'eau. Archived fromthe originalon 3 March 2016.Retrieved12 June2016.
- ↑"Selle ou Somme (E6420600)"(in French). SANDRE - Portail national d'accès aux référentiels sur l'eau. Archived fromthe originalon 3 March 2016.Retrieved12 June2016.
- ↑"Rivière du Saint-Landon (E6450600)"(in French). SANDRE - Portail national d'accès aux référentiels sur l'eau. Archived fromthe originalon 3 March 2016.Retrieved12 June2016.
- ↑"Rivière d'Airaines (E6450800)"(in French). SANDRE - Portail national d'accès aux référentiels sur l'eau. Archived fromthe originalon 3 March 2016.Retrieved12 June2016.
- ↑"Omignon (E6350750)"(in French). SANDRE - Portail national d'accès aux référentiels sur l'eau. Archived fromthe originalon 12 November 2014.Retrieved24 June2014.
- ↑"Cologne (E6350850)"(in French). SANDRE - Portail national d'accès aux référentiels sur l'eau. Archived fromthe originalon 12 November 2014.Retrieved24 June2014.
- ↑"Tortille (E6350900)"(in French). SANDRE - Portail national d'accès aux référentiels sur l'eau. Archived fromthe originalon 3 March 2016.Retrieved24 June2014.
- ↑"Ancre (E6380600)"(in French). SANDRE - Portail national d'accès aux référentiels sur l'eau. Archived fromthe originalon 3 March 2016.Retrieved12 June2016.
- ↑"Rivière d'Hallue (E6390700)"(in French). SANDRE - Portail national d'accès aux référentiels sur l'eau.Retrieved12 June2016.
- ↑"Nièvre (E6450650)"(in French). SANDRE - Portail national d'accès aux référentiels sur l'eau. Archived fromthe originalon 3 March 2016.Retrieved12 June2016.
- ↑"Scardon (E6480600)"(in French). SANDRE - Portail national d'accès aux référentiels sur l'eau. Archived fromthe originalon 3 March 2016.Retrieved12 June2016.
Other websites
[change|change source]- Banque Hydro - MEDDE, «Synthèse de la Banque Hydro»Archived2022-01-07 at theWayback Machine(in French)
