Earth radius
TheEnglishused in this article or sectionmay not be easy for everybody to understand.(May 2023) |
Earth radius(represented asR🜨or) is the distance from the center ofEarthto a point on or near its surface. Approximating thefigure of Earthby anEarth spheroid,the radius ranges from a maximum of nearly 6,378 km (3,963 mi) (equatorial radius,representeda) to a minimum of nearly 6,357 km (3,950 mi) (polar radius,representedb).
| Earth radius | |
|---|---|
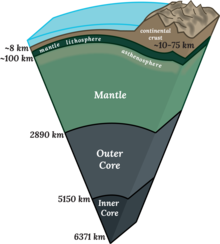 Cross section of Earth's Interior | |
| General information | |
| Unit system | astronomy,geophysics |
| Unit of | distance |
| Symbol | R🜨 or , |
| Conversions | |
| 1R🜨in... | ... is equal to... |
| SI base unit | 6.3781×106m[1] |
| Metric system | 6,357 to 6,378 km |
| English units | 3,950 to 3,963 mi |
Earth radius is sometimes used as aunit of measurementinastronomyandgeophysics.TheInternational Astronomical Unionrecommends that the radius at the equator should be used.
A globally-average value is usually believed to be 6,371 kilometres (3,959 mi) with a 0.3% variability (±10 km) for the following reasons. TheInternational Union of Geodesy and Geophysics(IUGG) provides three reference values: themean radius(R1) of three radii measured at two equator points and a pole; theauthalic radius,which is the radius of a sphere with the same surface area (R2); and thevolumetric radius,which is the radius of aspherehaving the same volume as theellipsoid(R3). All three values are about 6,371 kilometres (3,959 mi).
Other ways to define and measure the Earth radius involve theradius of curvature.A few definitions yield values outside the range betweenpolarradius andequatorialradius because they include local orgeoidaltopographyor because they depend on abstract geometrical that are carefully thought about.
References[change|change source]
- ↑Mamajek, E. E; Prsa, A; Torres, G; et al. (2015). "IAU 2015 Resolution B3 on Recommended Nominal Conversion Constants for Selected Solar and Planetary Properties".arXiv:1510.07674[astro-ph.SR].


