Temple of Artemis

TheTemple of Artemis(Greek:ἈρτεμίσιονorLatin:Artemisium), was a temple dedicated to the goddessArtemis.It was also known as the Temple of Diana (Dianawas a Roman goddess).
It was completed around350 BCatEphesus(in present-dayTurkey). The area was under theAchaemenid dynastyof thePersian Empire,but some of its cities were Greek. Only ruins of the temple remain. It was one of theSeven Wonders of the Ancient World.
Location[change|change source]
The Temple of Artemis was near the ancient city ofEphesus,about 50 km south from the modern port city ofİzmir,in Turkey.
Architecture and art[change|change source]
Most of the description of the Temple of Artemis comes fromPliny,though there are different accounts that give different sizes.
Pliny said the temple was 115 meters long and 55 meters wide. He said it was made almost completely ofmarble.It was about three times as big as theParthenonby area. The Temple has 127Ionic-styled columns. Each is 17.5 meters in height.
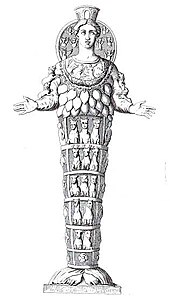
The Temple of Artemis had many fine artworks. Bronze sculptures by famous GreeksculptorsPolyclitus,Pheidias,Cresilas,andPhradmonwere in the temple. Paintings and gilded columns of gold and silver were also in it. The sculptors often competed at creating the best sculpture. Many of these sculptures were ofAmazons,who are said to have founded the city of Ephesus.
Pliny said thatScopas,who also worked on theMausoleum of Mausollos,worked carved reliefs into the temple's columns.
Athenagoras of AthensnamesEndoeus,a student ofDaedalus,as the sculptor of the main statue of Artemis in Ephesus.
Cult and influence[change|change source]
The Temple of Artemis was at a flourishing region. It was used as a religious institute.Merchantsand travellers came to it from all overAsia Minor.The temple was influenced by many beliefs. It can be seen as a symbol of faith for many different peoples. The Ephesians worshipedCybele.They joined many of their beliefs into the worship of Artemis. Artemisian Cybele became very different from the Roman goddessDiana.Thecultof Artemis attracted thousands of worshipers from far-off lands. They all gathered at the site and worshipped her.
References[change|change source]
- Anton Bammer, "A Peripteros" of the Geometric Period in the Artemision of Ephesus "Anatolian Studies40(1990), pp. 137–160.
- Lynn R. LiDonnici, "The Images of Artemis Ephesia and Greco-Roman Worship: A Reconsideration"The Harvard Theological Review85.4 (October 1992), pp 389–415.
Other websites[change|change source]
- UnMuseum'sThe Temple of Artemis
- Seven Wonders'Temple of ArtemisArchived2005-09-30 at theWayback Machine
- Florence Mary Bennett,Religious Cults Associated with the Amazons:(1912):Chapter III: Ephesian Artemis (text)
- James Grout:Temple of Artemis,part of the Encyclopædia Romana
- Diana's Temple at Ephesus(W. R. Lethaby, 1908)

