Atlantic Standard Time Zone
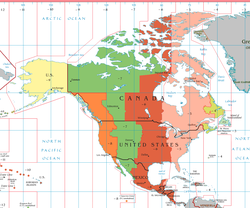
TheAtlantic Standard Time Zone (AST)is a geographic region that keepstimeby subtracting four hours from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), resulting in GMT-4 (UTC-4). The clock time in this zone is based on themean solar timeof the 60th degreemeridianwest of theGreenwich Observatory.
TheCanadianprovincesofNew Brunswick,Nova ScotiaandPrince Edward Islandkeep time by subtracting four hours from UTC. So doesBermuda,an islandterritoryin theNorth Atlantic.In the summer, both places usedaylight saving time.They keepAtlantic Daylight Time (ADT)(UTC-3) in the summer.
Other parts of the world that keep time by subtracting four hours from UTC include: manyCaribbeanislands, includingPuerto Rico,theU.S. Virgin Islands,and severalSouth Americancountries, such asParaguay,Chile,Bolivia,and parts ofBrazil.Venezuelaused AST until December 9, 2007, when it switched toUTC-4:30,but switched back to AST on May 1, 2016, at 2:30 a.m. local time.[1]
References
[change|change source]- ↑"Clocks to Go Forward Permanently in Venezuela".Time and Date.April 18, 2016.RetrievedApril 19,2016.
Other websites
[change|change source]- World time zone mapArchived2015-12-24 at theWayback Machine
- U.S. time zone mapArchived2009-02-15 at theWayback Machine
- History of U.S. time zones and UTC conversionArchived2004-10-12 at theWayback Machine
- Canada time zone map
- Time zones for major world cities
- Official times across Canada
- The official U.S. time for the Atlantic Time Zone (no DST)Archived2014-06-03 at theWayback Machine
