Journal Description
Medical Sciences Forum
Medical Sciences Forum
is an open access journal dedicated to publishing findings resulting from academic conferences, workshops and similar events in all areas of medical sciences, for advances in basic, translational and clinical research and related disciplines. The conference organizers and proceedings editors are responsible for managing the peer-review process and selecting papers for conference proceedings.
Latest Articles
Nutritional Protein Value of Flours via LC-MS/MS Analysis
Med. Sci. Forum2023,23(1), 10;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2023023010- 20 Sep 2024
Abstract
The growth of the world’s population and the reduction in the average annual global individual carbon footprint are current issues. With the aim of assessing nutritional protein values, we developed a sensitive analytical methodology for the identification and quantification of amino acids. Strategies
[...] Read more.
The growth of the world’s population and the reduction in the average annual global individual carbon footprint are current issues. With the aim of assessing nutritional protein values, we developed a sensitive analytical methodology for the identification and quantification of amino acids. Strategies have been developed to reduce sample complexity and improve detection for analysis by liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The method is suitable for the purpose and is a useful tool for protein value assessment, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 1st International Meeting Molecules 4 Life)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessProceeding Paper
The Epidemiology of Hepatitis in the Marche Region (Italy): A Notification System over a Decade (2012–2021)
by
Cosimo Damiano Giorgio Mangino,Corinna Fortunato,Love Chibuzor Ilochonwu,Andrea Mazzacchera,Davide Mengarelli detto Rinaldini,Giulia Mercante,Andrea PaladiniandFabio Filippetti
Med. Sci. Forum2024,25(1), 12;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025012- 29 Aug 2024
Abstract
The World Health Organization has highlighted the substantial impact of viral hepatitis on individuals, healthcare systems, and economies worldwide. This study’s objective is to monitor disease notifications to assess their trends. Data from infectious disease notifications detected in the Marche Region (Italy) were
[...] Read more.
The World Health Organization has highlighted the substantial impact of viral hepatitis on individuals, healthcare systems, and economies worldwide. This study’s objective is to monitor disease notifications to assess their trends. Data from infectious disease notifications detected in the Marche Region (Italy) were analyzed and entered into the Nuovo Sistema Informativo Sanitario portal between 1 January 2012 and 31 December 2021. In this period, there were 399 confirmed reports, of which 47.9% were for hepatitis A, 26.8% were for hepatitis B, 7% were for hepatitis C, and 18.3% were for hepatitis E; 67.4% of the afflicted individuals were male, and the average age was 43.5 years old. The year with the highest peak was 2017, accounting for 18% of the reports, while the year with the lowest number was 2020, followed by 2021, accounting for 3.8% and 4.5%, respectively. Effective surveillance systems are key to combating the spread of hepatitis and reducing its impact, although they have been affected by the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, with many cases remaining undetected.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2nd International One Health Conference)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessConference Report
Abstracts of the 2023 Autumn Meeting of the British Society for Cardiovascular Research
by
Carolyn Carr
Med. Sci. Forum2024,27(1), 3;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024027003- 28 Aug 2024
Abstract
The Autumn Meeting of the British Society for Cardiovascular Research in 2023 was organized by Carolyn Carr, Lisa Heather and Claudia Montes Aparicio at Wadham College at the University of Oxford and was the 50th Anniversary Meeting of the Society. The theme of
[...] Read more.
The Autumn Meeting of the British Society for Cardiovascular Research in 2023 was organized by Carolyn Carr, Lisa Heather and Claudia Montes Aparicio at Wadham College at the University of Oxford and was the 50th Anniversary Meeting of the Society. The theme of the meeting was “The impact of dysregulated metabolism on cardiovascular function” and included an early career symposium on “Life in academia and beyond”. The Annual Bernard and Joan Marshall Distinguished Investigator Lecture was given by Professor Doug Lewandowski on “Metabolic flux in the driver’s seat during cardiac health and disease”. This paper presents the abstracts selected for oral and poster presentation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2021/2022/2023 Autumn Meeting of the British Society for Cardiovascular Research)
Open AccessConference Report
Abstracts of the 2022 Autumn Meeting of the British Society for Cardiovascular Research
by
Carolyn Carr
Med. Sci. Forum2024,27(1), 2;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024027002- 26 Aug 2024
Abstract
The Autumn Meeting of the British Society for Cardiovascular Research in 2022 was organized by David Grieve, Lauren Kerrigan, Claire Tonry and Chris Watson and held at the Wellcome-Wolfson Institute for Experimental Medicine, Queen’s University Belfast. The theme of the meeting was ‘Cardiac
[...] Read more.
The Autumn Meeting of the British Society for Cardiovascular Research in 2022 was organized by David Grieve, Lauren Kerrigan, Claire Tonry and Chris Watson and held at the Wellcome-Wolfson Institute for Experimental Medicine, Queen’s University Belfast. The theme of the meeting was ‘Cardiac remodeling—basic mechanisms to clinical management’ and included an early career symposium. The Annual Bernard and Joan Marshall Distinguished Investigator Lecture was given by Professor Merry Lindsey on ‘Extracellular matrix remodeling in heart failure’. This paper presents the abstracts selected for oral and poster presentation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2021/2022/2023 Autumn Meeting of the British Society for Cardiovascular Research)
Open AccessConference Report
Abstracts of the 2021 Autumn Meeting of the British Society for Cardiovascular Research
by
Carolyn Carr
Med. Sci. Forum2024,27(1), 1;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024027001- 23 Aug 2024
Abstract
The Autumn Meeting of the British Society for Cardiovascular Research in 2021 was a virtual meeting organised by Andrew Bond, Anita Thomas, Elisa Avolio, Michele Carrabba, Raimondo Ascione, and Paolo Madeddu of the Bristol Medical School. The theme of the meeting was ‘Tissue
[...] Read more.
The Autumn Meeting of the British Society for Cardiovascular Research in 2021 was a virtual meeting organised by Andrew Bond, Anita Thomas, Elisa Avolio, Michele Carrabba, Raimondo Ascione, and Paolo Madeddu of the Bristol Medical School. The theme of the meeting was ‘Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine in cardiovascular disease’ and included an early career symposium. The Annual Bernard and Joan Marshall Distinguished Investigator Lecture was given by Professor Toshiharu Shinoka. This paper presents the abstracts selected for oral and poster presentations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2021/2022/2023 Autumn Meeting of the British Society for Cardiovascular Research)
Open AccessEditorial
Preface: The 3rd International Electronic Conference on Antibiotics
by
Marc Maresca
Med. Sci. Forum2024,24(1), 21;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024024021- 14 Aug 2024
Abstract
This volume presents a collection of contributions at the 3rd International Electronic Conference on Antibiotics held on 1–15 December 2023 [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 3rd International Electronic Conference on Antibiotics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Statement of Peer Review
by
Marc Maresca
Med. Sci. Forum2024,24(1), 20;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024024020- 14 Aug 2024
Abstract
In submitting conference proceedings toMedical Sciences Forum,the volume editors of the proceedings certify to the publisher that all papers published in this volume have been subjected to peer review administered by the volume editors [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 3rd International Electronic Conference on Antibiotics)
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Promoting Sustainable Agriculture: Impacts of Innovative Soil Management Approaches on Human Health and Ecosystems
by
Maria Vittoria Di Loreto,Simone Grasso,Francesco Lodato,Giorgio Pennazza,Luca VolleroandMarco Santonico
Med. Sci. Forum2024,25(1), 11;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025011- 7 Aug 2024
Abstract
Soil use and its proper management are key elements of sustainable development. However, given the complexity of the issue, it is necessary to address it using an interdisciplinary approach. The proposed work aims to analyze the consequences, in terms of damage assessment, of
[...] Read more.
Soil use and its proper management are key elements of sustainable development. However, given the complexity of the issue, it is necessary to address it using an interdisciplinary approach. The proposed work aims to analyze the consequences, in terms of damage assessment, of two different soil management systems of a cereal crop through the use of Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) methodology. One system follows a traditional approach and the other utilizes a Decision Support System (DSS). The long-term impacts on human health, ecosystems, and resource availability are calculated by employing the ReCiPe 2016 endpoint method. The results show notable reductions in resource use and environmental impacts with DSS, with a 41% decrease in damage to human health, a 24% reduction in ecosystem damage, and a 23% reduction in resource use. Hence, implementing new technologies and new management strategies in agriculture can lead to more sustainable management choices and can avoid long-term burdens compared to a traditional approach.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2nd International One Health Conference)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Participative Dimension: “Leave No One Behind”
by
Paula Sol Ventura,Marina Romeo,Sergi Valera,Jordi Serrano,Carolina Belenger-Hurtado,Felip Miralles,Joima Panisello,Maria Lledó-Cisneros,Irene Baños-Ruiz,Cristina Romera-Castillo,Francesc Font Rovira,Sonia Hernandez-Montaño-Bou,Daniel Turon,Domenico VitoandFernando Valladares
Med. Sci. Forum2024,25(1), 10;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025010- 24 Jun 2024
Abstract
Numerous authors emphasize climate change’s profound impact on physical, mental, and community health, particularly highlighting the rising concern of ecological anxiety. The participatory dimension of the KOSMA Observatory, “Leaving No One Behind”, sought to explore this issue. Initially, we presented Spain’s perceptions and
[...] Read more.
Numerous authors emphasize climate change’s profound impact on physical, mental, and community health, particularly highlighting the rising concern of ecological anxiety. The participatory dimension of the KOSMA Observatory, “Leaving No One Behind”, sought to explore this issue. Initially, we presented Spain’s perceptions and trends of eco-anxiety, along with the utilized platform. Subsequently, a roundtable delved into eco-anxiety and emotions, followed by a panel showcasing practical examples of transforming emotions into positive actions. The session concluded with a final reflection on these ideas.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2nd International One Health Conference)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Barrio Logan Case Study: Modern Environmental Injustice
by
Marco Nunez MoctezumaandGabriela Fernandez
Med. Sci. Forum2024,25(1), 9;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025009- 10 May 2024
Abstract
Barrio Logan is a Mexican American community in San Diego in which industrial companies and residences share a space enclosed by a bay and an interstate. Ever since WWII, the Barrio Logan community has faced environmental injustice. There is a gap in Barrio
[...] Read more.
Barrio Logan is a Mexican American community in San Diego in which industrial companies and residences share a space enclosed by a bay and an interstate. Ever since WWII, the Barrio Logan community has faced environmental injustice. There is a gap in Barrio Logan’s ability to self-monitor, so business models were developed to bring forth citizen science projects based on data collected from government environmental studies, the nurse’s office at Barrio Logan’s Perkins K-8 School, and interviews with Perkins K-8 School’s principal and the director and staff at the Chicano Park Museum and Cultural Center. It was found that children in Barrio Logan are experiencing a health crisis. Homelessness, single-parent households, unemployment, gentrification, low-wage jobs, continuous diesel particulate matter exposure, and high levels of asthma can be found in Barrio Logan. There is a lack of easily accessible, community-wide health programs that address ACEs and a lack of air pollution monitoring.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2nd International One Health Conference)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Isolation of Multiresistant Bacterial Strains from Dairy Wastewater: A Public Health Concern in a One Health Perspective
by
Caterina Elisabetta Rizzo,Paola Tripodi,Isabella La Spina,Maria Eufemia Gioffrè,Antonino Virga,Alessio FacciolàandPasqualina Laganà
Med. Sci. Forum2024,25(1), 8;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025008- 9 May 2024
Abstract
The use of antibiotics in the veterinary and zootechnic sectors poses a challenge to the reduction in antibiotic resistance rates. We evaluated the presence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the wastewater of dairy farms in the Sicily Region, Italy. The samples were examined by
[...] Read more.
The use of antibiotics in the veterinary and zootechnic sectors poses a challenge to the reduction in antibiotic resistance rates. We evaluated the presence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the wastewater of dairy farms in the Sicily Region, Italy. The samples were examined by isolating and identifying the bacterial strains, which were then tested for the main classes of antibiotics.Aeromonasspp. andVibriospp. were the more commonly isolated strains (18.2%), followed byPseudomonasspp. (15.9%),Enterobacterspp. andCitrobacterspp. (13.6%). Macrolides were the drugs against which the highest resistance was detected, followed by tetracyclines, penicillins, and cephalosporins. The agri-food chain and zootechnic areas embody an important source of bacteria resistant to antibiotics, and their presence in wastewater from processing factories could play a pivotal role in spreading these microorganisms and in environmental contamination.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2nd International One Health Conference)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Climate Crises Associated with Epidemiological, Environmental, and Ecosystem Effects of a Storm: Flooding, Landslides, and Damage to Urban and Rural Areas (Extreme Weather Events of Storm Daniel in Thessaly, Greece)
by
Ioannis Adamopoulos,Aikaterini FrantzanaandNiki Syrou
Med. Sci. Forum2024,25(1), 7;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025007- 8 May 2024
Cited by 5
Abstract
The effects of climate crises and disasters must be managed appropriately. These effects can have a considerable influence on public health. This issue relates to epidemiological models and policy regarding climate factors, such as temperature, precipitation, humidity, and health results. Historical data were
[...] Read more.
The effects of climate crises and disasters must be managed appropriately. These effects can have a considerable influence on public health. This issue relates to epidemiological models and policy regarding climate factors, such as temperature, precipitation, humidity, and health results. Historical data were analyzed so that patterns and connections between climatic factors and health outcomes could be found. Epidemiological models were used to simulate the spread of illnesses. Climate variables were used as inputs to these models to determine their effect on the spread of disease. This study examines the current public health regulations concerning epidemiology, climate change, and establishing new policies or revising existing ones to address the issues found to protect public health. To conclude, immediate efforts are needed to save human lives, protect vulnerable wildlife, and improve public health. Ecological assessments need to be conducted to understand extreme weather events (such as Storm Daniel), monitor ecosystem recovery, and adapt management strategies as needed, as well as to develop disaster preparedness to reduce future risks.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2nd International One Health Conference)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Developing a Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG3) Index for Italian Municipalities
by
Julia Nawaro,Lorenzo GianquintieriandEnrico G. Caiani
Med. Sci. Forum2024,25(1), 6;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025006- 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
Since the establishment of the SDGs, related progress at a national level has usually been measured using the province as the smallest geographical aggregation. To cope with this gap, we aimed to develop a methodology for SDG3 index calculation for Italian municipalities. Official
[...] Read more.
Since the establishment of the SDGs, related progress at a national level has usually been measured using the province as the smallest geographical aggregation. To cope with this gap, we aimed to develop a methodology for SDG3 index calculation for Italian municipalities. Official data for 2018–2022 were collected to cover 11 of 13 SDG3 targets that were mapped to 29 unique indicators: 10 were computed at municipal level, while for the remaining 19 a lower granularity was applied. The SDG3 index, calculated by weighting the targets equally, ranged from 0 to 1, with higher values corresponding to better goal fulfilment. The methodology was applied to the municipalities in the Lombardy region, where the index spanned 0.538 to 0.769. Since SDG indices contribute to the 2030 Agenda goal achievements at country level, more attention should be paid to the geographical details of assessment through policy information and local benchmarking.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2nd International One Health Conference)
►▼
Show Figures
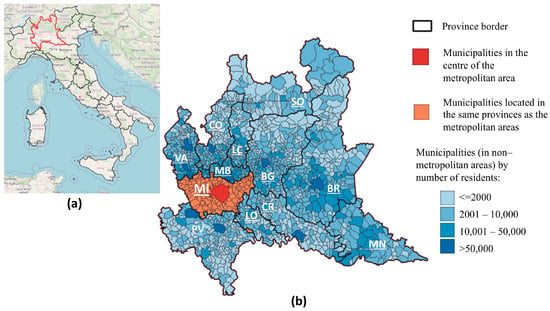
Figure 1
Open AccessConference Report
Preface and Abstracts of the 2nd International One Health Conference
by
Margherita Ferrante,Gea Oliveri Conti,Domenico Vito,Gabriela Fernandez,Carol Maione,Paolo Lauriola,Prisco Piscitelli,Melissa Jimenez Gomes Tagle,Carlos Dora,Jordi Serrano Pons,Carole Conforti,Joima Panisello,Paula Sol Ventura,Ilaria Bernotti,Carmen Ruiz Martin,Edgar Buloz,Marcella Trombetta,Giuseppe BanfiandValentina Tageo
Med. Sci. Forum2024,25(1), 5;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025005- 15 Apr 2024
Abstract
The International One Health Conference 2023, scheduled for October in Barcelona, fosters a collaborative, multidisciplinary approach to health involving professionals, academics, and decision-makers. Operating in a hybrid format, the conference aims to bridge the gap between scientific knowledge and policies, aligning with the
[...] Read more.
The International One Health Conference 2023, scheduled for October in Barcelona, fosters a collaborative, multidisciplinary approach to health involving professionals, academics, and decision-makers. Operating in a hybrid format, the conference aims to bridge the gap between scientific knowledge and policies, aligning with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Health in All Policies (HiAP). Emphasizing community involvement and the symbiotic relationship between basic needs, sustainable lifestyles, and empowerment, the conference envisions a comprehensive approach to sustainable development. D’Alisa introduces a framework incorporating participative democracy, recognizing the interconnectedness of economic, social, environmental, and participative democratic dimensions. Framing questions for the conference delve into critical aspects, addressing the integration of the One Health framework within health sectors, emphasizing interlinkages between health, climate change, and decision-making. The conference’s five-dimension framework tackles the complexity of One Health, addressing concerns, solutions, and opportunities in a holistic paradigm.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2nd International One Health Conference)
►▼
Show Figures
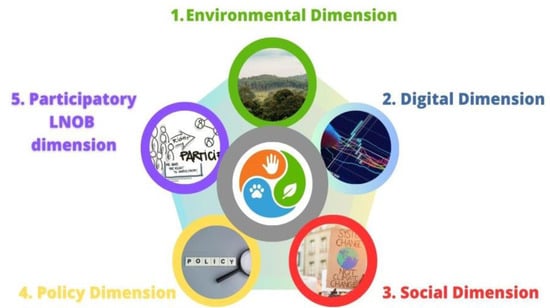
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Preface: The 1st International Electronic Conference on Vaccines—RNA Vaccines, Current Challenges and Future Developments
by
François MeurensandFanny Renois
Med. Sci. Forum2024,26(1), 5;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024026005- 8 Apr 2024
Abstract
The 1st International Electronic Conference on Vaccines: RNA Vaccines, Current Challenges and Future Developments (IECV 2023), was held on 1–15 December 2023 [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 1st International Electronic Conference on Vaccines)
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Understanding “Eco Anxiety” in Adolescents and Young Adults
by
Julie Garcia Souza
Med. Sci. Forum2024,25(1), 4;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025004- 6 Mar 2024
Abstract
As environmental issues become more complex, so do our emotional responses to them. Paul Robbins and Sarah A. Moore offer the term “ecological anxiety” to frame scholarly discourse around a fearful response to the “negative normative influence of humans on the earth” and
[...] Read more.
As environmental issues become more complex, so do our emotional responses to them. Paul Robbins and Sarah A. Moore offer the term “ecological anxiety” to frame scholarly discourse around a fearful response to the “negative normative influence of humans on the earth” and the “inherent influence of normative human values within one’s own science”. This comprehensive literature review unpacks the implications of “eco anxiety” within. The eco anxiety framework is relatively new, with minimal consensus on symptomatic criteria. To appropriately reflect the thoughts, emotions, and experiences of adolescents and young adults, this literature review encourages more accessible climate communication for the sake of the public and science community. Furthermore, more avenues of research are needed to study the term eco anxiety to fit a global context extending beyond Western understanding.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2nd International One Health Conference)
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Synthesis of Lignin Nanoparticles: Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approaches
by
Rossella Grappa,Virginia Venezia,Brigida Silvestri,Aniello CostantiniandGiuseppina Luciani
Med. Sci. Forum2024,25(1), 3;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025003- 26 Feb 2024
Abstract
Lignin, a main byproduct from paper manufacturing and biorefineries, is now emerging as a new low-cost, renewable starting material for new product development. Its biocompatibility and safety make it valuable for creating novel and value-added products. Lignin, a polymer with many hydrophilic and
[...] Read more.
Lignin, a main byproduct from paper manufacturing and biorefineries, is now emerging as a new low-cost, renewable starting material for new product development. Its biocompatibility and safety make it valuable for creating novel and value-added products. Lignin, a polymer with many hydrophilic and active groups, confers many useful properties. However, there are several challenges to overcome due to its complex chemical structure and heterogeneous self-assembly behavior. Nanostructured systems using lignin could address these challenges, finding applications in food science, cosmetics, and healthcare. This study explores two main green synthesis approaches for lignin nanoparticles: bottom-up based on the self-assembly in a solvent–antisolvent system and top-down based on the ultrasonication. These nanoparticles are evaluated for morphology, estimation of phenolic content and antioxidant effects. Specifically, the antisolvent nanostructures show a spherical conformation with a higher antioxidant activity due to a better organization of phenolic hydroxyl groups. Obtained result have been exploited to draw an efficient and cheap technological route for lignin valorization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2nd International One Health Conference)
►▼
Show Figures
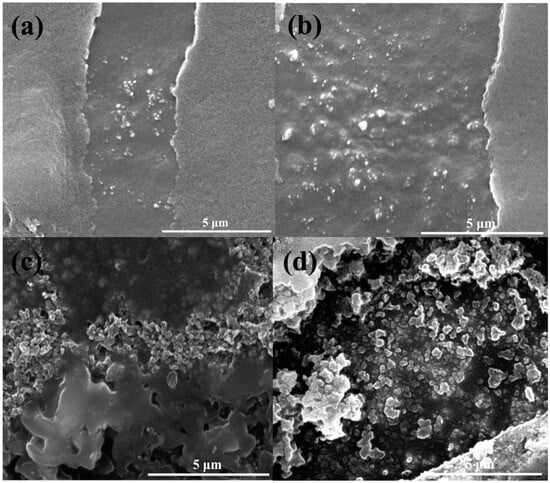
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Towards a One Health Assessment of Artisanal and Informal Mining in Benue State, Nigeria
by
Samuel N. Paul,Chiara FrazzoliandOrish E. Orisakwe
Med. Sci. Forum2024,25(1), 2;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025002- 22 Feb 2024
Abstract
This study evaluated the eco-health risk associated with exposure to lead (Pb) in mining sites in Benue State, Nigeria. Lead contamination was assessed in 48 water samples and 40 human blood samples. An Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer was used for Pb analysis and ELISA
[...] Read more.
This study evaluated the eco-health risk associated with exposure to lead (Pb) in mining sites in Benue State, Nigeria. Lead contamination was assessed in 48 water samples and 40 human blood samples. An Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer was used for Pb analysis and ELISA kits for tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) analysis. A correlation was found between the blood Pb level (BLL) and the upregulation of KIM-1. The BLL of females was slightly higher than males, resulting in a higher inflammatory response through increased TNF-α levels. An increased inflammatory response due to chronic Pb exposure was observed with age. Miners and farmers around the mining sites recorded higher TNF-α levels compared to businesspeople, thus suggesting direct exposure to other mining-associated contaminants. Artisanal and informal mining impact environmental health and the Pb body burden.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2nd International One Health Conference)
►▼
Show Figures
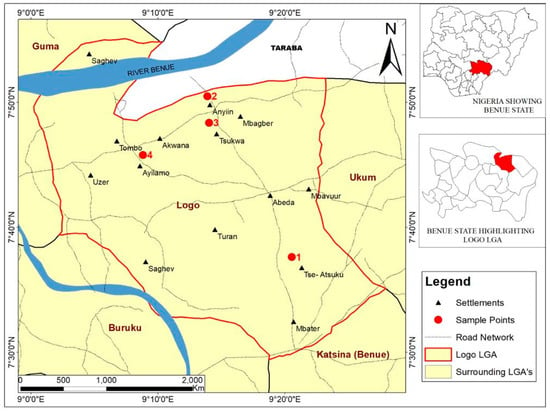
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Public Health Implications of Antimicrobial Resistance in Wildlife at the One Health Interface
by
Julio A. Benavides,Marilia Salgado-Caxito,Carmen TorresandSylvain Godreuil
Med. Sci. Forum2024,25(1), 1;https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2024025001- 31 Jan 2024
Cited by 1
Abstract
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) such as extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing and carbapenem-resistant (CARBA)Enterobacteralesis a main global cause of human deaths and a major health burden to domestic animals. AMR circulation in wildlife has also been reported worldwide, but the public health impact and
[...] Read more.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) such as extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing and carbapenem-resistant (CARBA)Enterobacteralesis a main global cause of human deaths and a major health burden to domestic animals. AMR circulation in wildlife has also been reported worldwide, but the public health impact and the policy actions that could limit this circulation remain unknown. Here, we summarize the key trends of AMR in wildlife, clarify the use of the term ‘reservoir’ when referring to AMR in wildlife, identify whether national plans to tackle AMR in Latin America and Europe include wildlife, and discuss the public health implications of this circulation. We provide recommendations for AMR surveillance and prevention among wild animals, as well as the key scientific knowledge gaps that are hindering understanding its dynamics. We expect our conclusions to shed light on the necessity and degree of prevention and control regarding AMR in wildlife at the human–animal–environment interface.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 2nd International One Health Conference)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Prevalence of Self-Medicated Use of Antibiotics among the Population in Ernakulam District in Kerala, India
by
Divya Nair,Padinchare Veettil GayathriandGirish Gopinath
Med. Sci. Forum2024,24(1), 13;https://doi.org/10.3390/ECA2023-16478- 26 Jan 2024
Abstract
Self-medication (SM) of antibiotics has become a prevalent reason for the development of antibiotic resistance. This study aims to assess the use of self-medication practices with antibiotics and related factors among the population of Ernakulam district, Kerala. Sore throat (34%) and cough (26%)
[...] Read more.
Self-medication (SM) of antibiotics has become a prevalent reason for the development of antibiotic resistance. This study aims to assess the use of self-medication practices with antibiotics and related factors among the population of Ernakulam district, Kerala. Sore throat (34%) and cough (26%) are found to be the major reasons for the self-usage of antibiotics among people. Various antibiotics commonly used for self-medication were amoxicillin, ciprofloxacin, and azithromycin. Reasons for the use of antibiotic self-medication were previous successful experiences (7.7%), convenience (11.5%), and to save costs (3.8%). Improper antibiotic use may lead to drug overuse and thereby antibiotic resistance. Hence, it should be taken only under strict supervision by an expert.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings ofThe 3rd International Electronic Conference on Antibiotics)
►▼
Show Figures
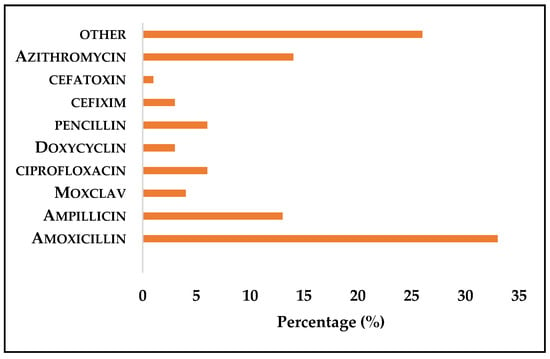
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics













